Calculation of Li-Ion Battery Electrolyte
Full-Atomistic Molecular Dynamics (FAMD) was used to evaluate the relationship between molecular structure and properties of battery electrolytes. Representative molecules (EC, DMC, PF₆) were modeled, and self-diffusion coefficients of Li⁺ ions in the bulk state and the effects of composition ratios were analyzed.
Use Cases Highlights
- Evaluation of molecular structure and properties of electrolytes
- Evaluation of Li⁺ ion diffusion coefficients
- Analysis of the effect of composition ratio
Molecular structure modeling
Representative molecular structures of EC, DMC, and PF₆ are modeled in J-OCTA. The COGNAC modeler allows setting and adjustment of force field parameters including point charges, with electrolyte-specific parameters incorporated.
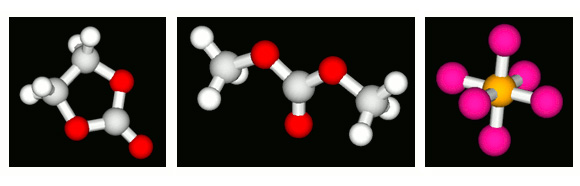
Molecular structure used in the calculation
Diffusion evaluation in bulk state
In the bulk state, the behavior of Li⁺ ions (shown as yellow particles) was analyzed using long-time relaxation calculations with Molecular Dynamics. The influence of self-diffusion coefficients and composition ratios of electrolyte components on diffusion can be evaluated.
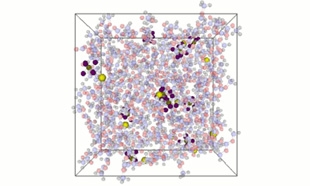
Bulk-state structure
Inquiries Regarding Products
Have questions about product implementation? Contact us today.