Gas Diffusion Analysis
Full-Atomistic Molecular Dynamics (FAMD) was used to evaluate the diffusivity of oxygen and carbon dioxide in PDMS and polyisoprene. For PDMS, this relates to the oxygen permeability of contact lenses; for polyisoprene, it relates to the gas barrier properties of tire materials. Differences in diffusivity due to temperature and molecular species were discussed.
Use Cases Highlights
- Structure creation using scenario functionality
- Evaluation of diffusion coefficients from molecular motion
- Evaluation of differences in diffusivity due to molecular species and temperature
Structure creation using the scenario function
Construction of amorphous PDMS and PI structures with gas molecules inserted using J-OCTA’s scenario function is shown.
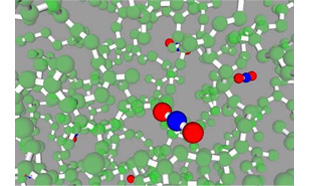
Oxygen molecules in PDMS
Evaluation of diffusion coefficient
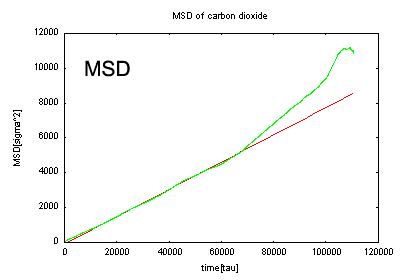
From gas molecule dynamics results, the mean square displacement (MSD) was evaluated. From its slope, the self-diffusion coefficient was calculated. Comparing the self-diffusion coefficients of oxygen and carbon dioxide, trends consistent with experimental data were obtained. The temperature dependence of diffusion coefficients was also evaluated.
Temperature dependence of diffusion coefficient
Reference
[1] Jie Han and Richard H. Boyd, Polymer, vol. 37, 10, pp. 1797, 1996
[2] Extracts from Polyinfo Database
[3] Y. Tamai, H. Tanaka and K. Nakanishi, Macromolecules, vol. 27, pp. 4498, 1994
[2] Extracts from Polyinfo Database
[3] Y. Tamai, H. Tanaka and K. Nakanishi, Macromolecules, vol. 27, pp. 4498, 1994
Details of analysis
Inquiries Regarding Products
Have questions about product implementation? Contact us today.