Calculation of solubility coefficient
The solubility coefficient of gas molecules in polymers was evaluated using J-OCTA’s solubility module. The Excluded Volume Map Sampling (EVMS) method was used to calculate excess chemical potential, from which solubility coefficients were derived. Solubility of gases (N₂, O₂, CO₂, CH₄) in various polymers and water was calculated, and good agreement with experimental values was confirmed.
Use Cases Highlights
- Calculation of solubility coefficients using excess chemical potential in the J-OCTA solubility module
- Evaluation of gas solubility in polymers
- Evaluation of gas barrier and gas permeability properties
Calculation of solubility coefficients in J-OCTA’s solubility module from excess chemical potential
Models of three polymers (PE, PS, PB) and water are shown for calculating gas solubility coefficients (N₂, O₂, CO₂, CH₄).
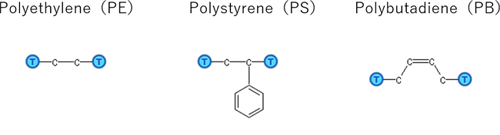
Model used in the calculation
Evaluation of gas solubility in polymers
A comparison between calculated solubility coefficients and experimental values is shown. High solubility in PS was observed, and CO₂ molecules tended to have higher solubility than other gases.
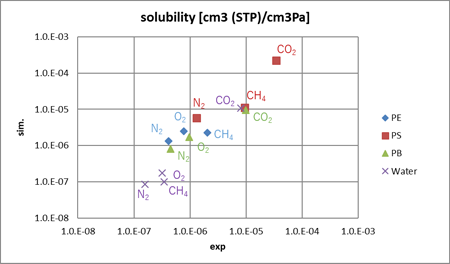
Comparison between calculated solubility coefficients and experimental values
Reference
[1] G. L. Deitrick,L.E.Scriven, and H.T.Davis, J. Chem. Phys., 90,2370 (1989)
[2] A. S. Michaels and H. J. Bixler, J. Polym. Sci., vol. 50, no. 154, pp. 393-412, 1961
[3] W. R. Vieth, P. M. Tam, and A. S. Michaels, J. Colloid Interface Sci., vol. 22, no. 4, pp. 360-370, 1966.
[4] Polymer Handbook
[5] R. Sander, Atmos. Chem. Phys., vol. 15, no. 8, pp. 4399-4981, 2015.
[2] A. S. Michaels and H. J. Bixler, J. Polym. Sci., vol. 50, no. 154, pp. 393-412, 1961
[3] W. R. Vieth, P. M. Tam, and A. S. Michaels, J. Colloid Interface Sci., vol. 22, no. 4, pp. 360-370, 1966.
[4] Polymer Handbook
[5] R. Sander, Atmos. Chem. Phys., vol. 15, no. 8, pp. 4399-4981, 2015.
Details of analysis
Inquiries Regarding Products
Have questions about product implementation? Contact us today.