Optical Properties
- Analysis of birefringence caused by molecular orientation
- Evaluation of the relationship between benzene ring orientation and refractive index
- Utilization for material design such as reducing birefringence by blending
Extension calculation results for polystyrene
Structure of polystyrene with benzene rings oriented perpendicular to elongation direction after uniaxial elongation is shown, explaining negative orientation birefringence.
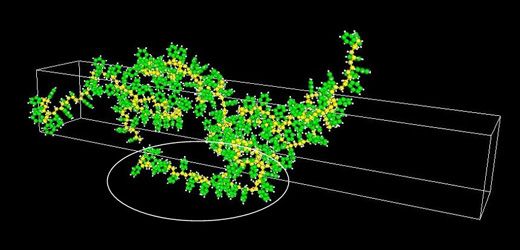
Uniaxial elongation calculation results for polycarbonate
The structure of polycarbonate (PC) in which benzene ring planes are oriented parallel to the elongation direction is shown. Since the refractive index in the ring plane direction is higher, positive birefringence is expected to occur.
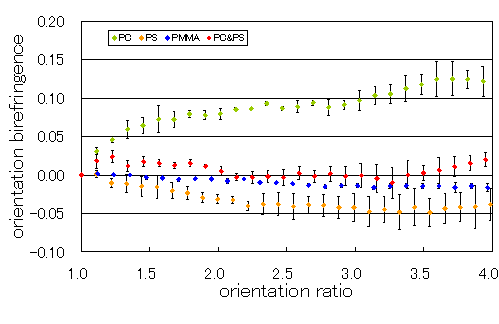
Comparison of orientation birefringence
Birefringence was evaluated using the scenario function in J-OCTA. From MD calculation results, vectors of all covalent bonds were obtained, and using a bond polarizability database, refractive indices in the X, Y, and Z directions were evaluated for the entire system. The orientation birefringence of PC, PS, PMMA, and PC/PS blends was compared: PC showed positive birefringence, PS negative, PMMA nearly zero, and blends showed reduced birefringence.
[2] (in Japanese) Iwashimizu, Okubo, Ozawa, Kimizuka, Molding Process Symposium '06, C-201, pp 107-108, (2006)