Effect of Surfactants for Interfacial Tension
Surfactants enable water and oil to mix (emulsification). Dissipative Particle Dynamics (DPD) simulations were performed with surfactants included at the interface, followed by relaxation calculations. It was evaluated that increasing surfactant density reduced interfacial tension and caused collapse of the interfacial shape.
Use Cases Highlights
- Analysis of interfacial tension using DPD
- Evaluation of the effect of surfactant density
- Evaluation of emulsification processes
Interface analysis using DPD
Effect of surfactant density on interfacial shape is shown. Higher density reduces interfacial tension and causes collapse of the interface.
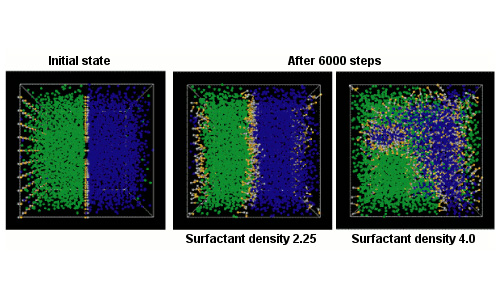
Change in interfacial shape by surfactants
Evaluation of interfacial tension
The relationship between surfactant density and interfacial tension is shown. Interfacial tension was calculated from stress values in each direction. As density increases, interfacial tension decreases, allowing evaluation of surfactant effects.
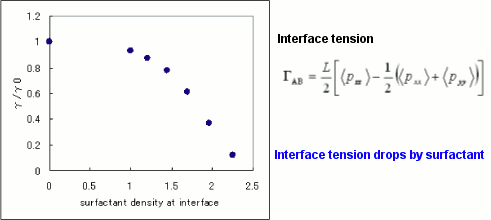
Relationship between surfactant amount and interfacial tension
Details of analysis
Inquiries Regarding Products
Have questions about product implementation? Contact us today.