Estimation of Property Values Using QSPR
Quantitative structure–property relationships (QSPR) were used to predict properties of amorphous polymers from molecular structure. The QSPR function in J-OCTA’s MI-Suite is not limited to machine learning models; it supports polymers composed of nine types of atoms and uses regression equations based on the Bicerano method to estimate density, heat capacity, dielectric constant, and glass transition temperature, confirming good correlation with experimental values.
Use Cases Highlights
- Estimation of physical property values from molecular structure
- Good correlation with experimental values
- Compatibility with various physical properties
Polymer structure targeted for evaluation
Molecular structures of five polymers evaluated are shown. These polymers have significantly different structures and were selected as property prediction targets. High-molecular-weight polymers without molecular weight dependence are targeted.
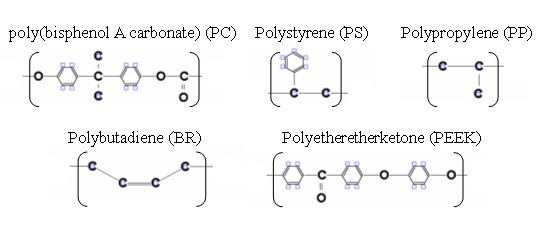
Monomer structures of five polymers
Evaluation of density
Densities of various polymers at room temperature were estimated using QSPR and compared with experimental values. The estimated values showed good agreement, supporting the reliability of the model.
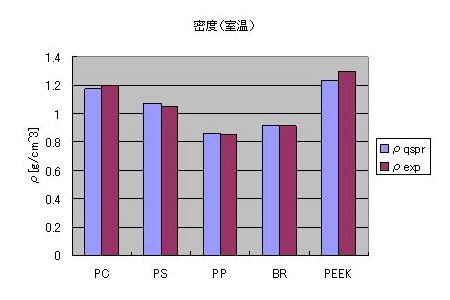
Density (room temperature)
Constant-pressure specific heat (room temperature)
The comparison of predicted and experimental constant-pressure heat capacity at room temperature is shown. QSPR predictions show high correlation with experimental values.
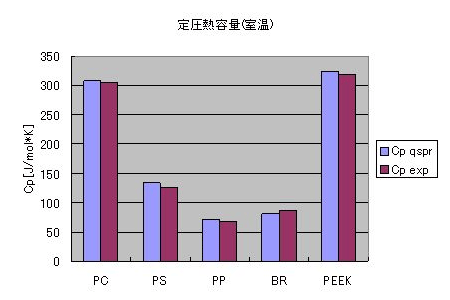
Constant-pressure specific heat (room temperature)
Reference
[1] Jozef Bicerano PREDICTION OF POLYMER PROPERTIES 3rd Ed Marcel Dekker 2002
[2] PolyInfo http://polymer.nims.go.jp/
[2] PolyInfo http://polymer.nims.go.jp/
Details of analysis
Inquiries Regarding Products
Have questions about product implementation? Contact us today.