Simulation of the deposition of film
In the vacuum deposition process used for creating organic devices such as OLEDs, the influence of molecular shape on molecular orientation in films was analyzed. Two types of molecules, TPD and BSP-Cz, were used, and the deposition process on silver substrates was reproduced by Molecular Dynamics (MD) simulations. It was found that BSP-Cz tends to adopt a vertical orientation to the substrate more easily, confirming that molecular structure affects film orientation.
Use Cases Highlights
- MD simulation of vacuum-deposited films for OLED applications
- Relationship between molecular structure and device performance
MD simulation of vapor-deposited films for OLED applications
Structures of two molecules, TPD and BSP-Cz, used for vacuum deposition film formation are shown. TPD has a nonlinear structure, and BSP-Cz has a linear structure, influencing molecular orientation in the film.
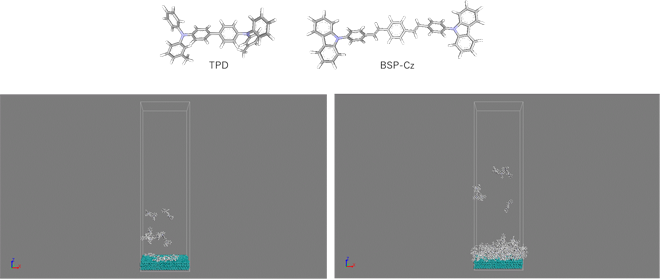
Top: Two types of molecules used in the calculation. Bottom: Deposition simulation of TPD (left: initial, right: later stage)
Relationship between molecular structure and device properties
The analysis results of the orientation order parameter P for evaluating molecular orientation in vapor-deposited films are shown. P = 1 indicates parallel to the reference axis, and P = –0.5 indicates perpendicular. It was found that BSP-Cz tends to adopt a configuration perpendicular to the Z-axis (parallel to the substrate) more readily, clearly showing the influence of molecular structure on ordering in films.
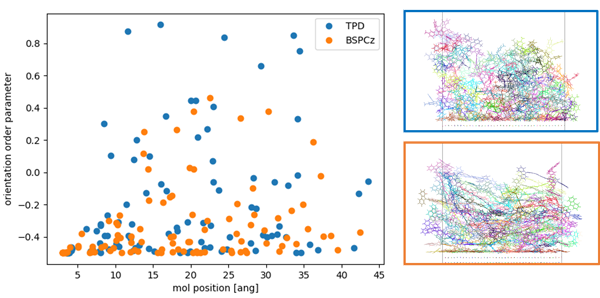
Left: Analysis results of orientation order parameter. Right: Structures of each molecule in deposited films (top: TPD, bottom: BSP-Cz)
Reference
[1] D. Yokoyama, Journal of Materials Chemistry, 21, 19187-19202, (2011)
[2] H. Heinz, et al., J. Phys. Chem. C, 112, 17281-17290, (2008)
[2] H. Heinz, et al., J. Phys. Chem. C, 112, 17281-17290, (2008)
Details of analysis
Related information
Inquiries Regarding Products
Have questions about product implementation? Contact us today.