Polymer/Solid Interface Peeling
The interfacial debonding between amorphous polyethylene (PE) and a graphite wall was analyzed using Full-Atomistic Molecular Dynamics (FAMD). An interfacial model created with J-OCTA’s modeling function was used, and debonding behavior was reproduced by moving the wall downward. Changes in stress and void formation were visualized.
Use Cases Highlights
- Reproduction of interfacial debonding by wall movement
- Evaluation of changes in vertical stress and void formation
- Easy modeling using J-OCTA functions
Construction of interfacial models
An interfacial model of polyethylene and graphite wall is constructed, with carbon atoms white and hydrogen atoms blue. Periodic boundaries are in X and Y, and reflective in Z.
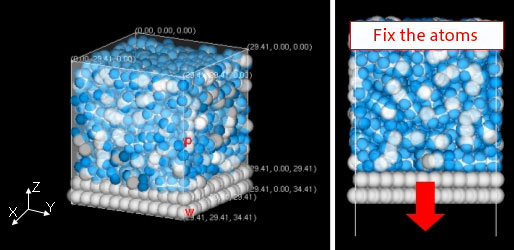
Interfacial model of polyethylene and graphite wall
Interfacial debonding process
The peeling process due to wall movement is illustrated. The detachment of polyethylene from a graphite substrate is shown.
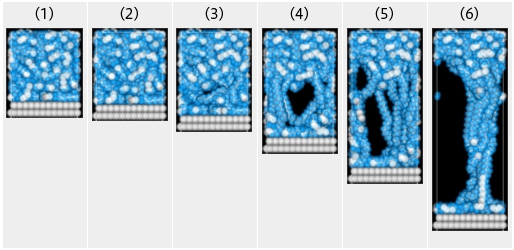
Visualization of peeling process
Evaluation of stress variations
A graph plotting normal stress versus wall displacement is shown. The numbering corresponds to the earlier figure, and a sharp change in stress with the progression of debonding can be observed.
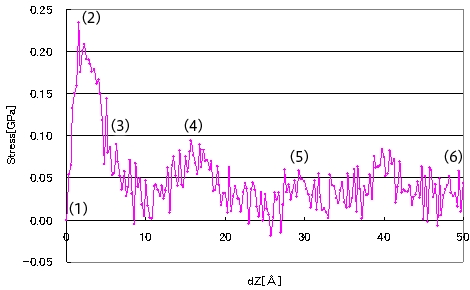
Change in wall stress during peeling process
Reference
[1] A.P.Awasthi, D. C. Langoudas and D. C. Hammerand, Modeling Simul. Mater. Sci. Eng. 17 (2009) 015002
Details of analysis
Related information
Inquiries Regarding Products
Have questions about product implementation? Contact us today.