Simulation of Solvent Evaporation Using DPD
COGNAC Dissipative Particle Dynamics (DPD) was used to represent two polymers, a solvent, and a gas phase. The evaporation phenomenon, in which the solvent component moves from a thin film composed of polymer and solvent to the gas phase region, was reproduced. The process of forming phase-separated structures transitioning from parallel to perpendicular orientation relative to the substrate during evaporation was confirmed, and the effects of interactions and wettability were evaluated.
Use Cases Highlights
- Evaluation of phase-separated structures with evaporation using DPD
- Evaluation of effects of evaporation rate and wettability
- Evaluation of phase separation in polymer thin films
Formation process of phase-separated structures during evaporation
The process in which two initially mixed polymers phase-separate during evaporation, first forming a parallel structure to the substrate and finally changing to a perpendicular structure, is shown.
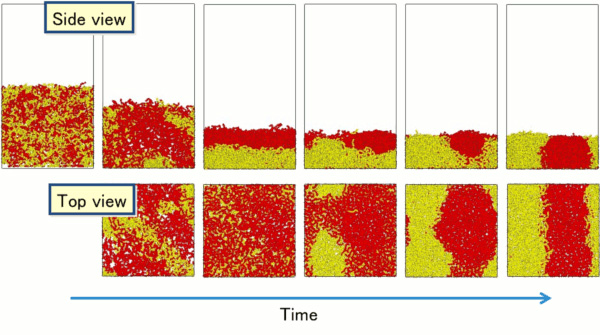
Phase separation in polymer thin films caused by solvent evaporation
Reference
[1] Nihon Reoroji Gakkaishi, Vol.36, 93-98
https://www.jstage.jst.go.jp/article/rheology/36/2/36_2_93/_pdf
https://www.jstage.jst.go.jp/article/rheology/36/2/36_2_93/_pdf
Details of analysis
Inquiries Regarding Products
Have questions about product implementation? Contact us today.