Formation of lipid bilayers and vesicles using FMODPD
FCEWS and Dissipative Particle Dynamics (DPD) were used to simulate vesicle formation of the phospholipid POPC. FCEWS, developed by the Mochizuki Laboratory at Rikkyo University, segments lipid molecules and predicts interaction parameters (χ parameters) with high accuracy. The lipid fraction was then varied in DPD simulations to reproduce lipid bilayer and vesicle formation. Membrane area and thickness showed good agreement with experimental values, and the approach is expected to be applicable to drug delivery system (DDS) design.
Use Cases Highlights
- Prediction of χ parameters using FCEWS and mesoscale analysis of phospholipids
- Analysis of the structural formation process of lipid membranes
Prediction of χ parameters using FCEWS and mesoscale analysis of phospholipids
A lipid molecule is segmented, and χ parameters between segments are predicted with high accuracy using FCEWS based on the Fragment Molecular Orbital (FMO) method. Four water molecules are represented as one DPD particle.
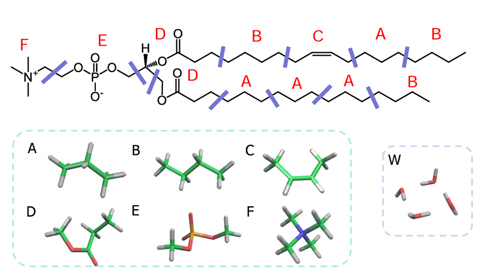
Segment division of POPC molecules
Analysis of structural formation processes in lipid membranes
The formation process of lipid membranes simulated using DPD is shown. Lipid molecules self-assemble to form bilayer or vesicle structures, and evaluation of membrane thickness and structural stability is possible.
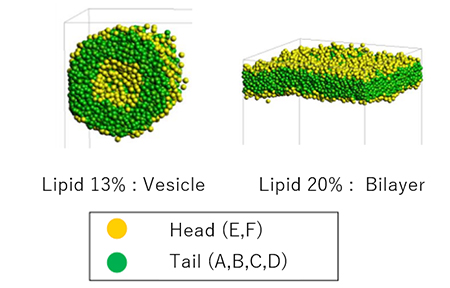
Formation process of lipid membranes by DPD
Reference
[1] Chem.Phys.Lett., 684, pp427-432, (2017)
[2] J.Phys.Chem.B, 122, pp338-347, (2018)
[2] J.Phys.Chem.B, 122, pp338-347, (2018)
Details of analysis
Inquiries Regarding Products
Have questions about product implementation? Contact us today.