Cross-Linked Structure of Thermosetting Resin
Coarse-Grained Molecular Dynamics (CGMD) was used to generate a three-dimensional network structure formed by the crosslinking reaction between epoxy monomers and curing agents. After the reaction, reverse mapping to a Full-Atomistic model was performed to evaluate physical properties such as density changes. The Coarse-Grained potential was determined using the COGNAC modeler, and the reaction calculation was carried out.
Use Cases Highlights
- Generation and evaluation of crosslinked structures of thermosetting resins using Coarse-Grained models
- Construction of Full-Atomistic model structures via reverse mapping
- Evaluation of properties of crosslinked structures
Crosslinking of epoxy resin using Coarse-Grained models
The crosslinking reaction process of epoxy resin in a Coarse-Grained model is shown, comparing intermediate and fully reacted states.
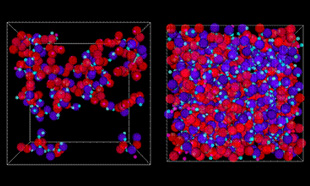
Crosslinking of epoxy resin by Coarse-Grained model
Evaluation of density change
The density of a monomer–hardener mixture before reaction was 0.91 [g/cm³], and after crosslink structure formation in the reaction, it increased to 1.28 [g/cm³]. Using J-OCTA’s modeling function, molecular structures of the Full-Atomistic model can be constructed from Coarse-Grained MD results via reverse mapping. Combining with the Coarse-Grained model enables initial structure construction considering long-time molecular behavior.
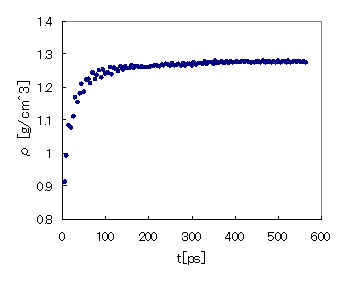
Increase in density due to crosslinking
Reference
[1] P.V.Komarov, C.Yu-Tsung, C. Shih-Ming, P. G. Khalatur and P. Reineker, Macromolecules, 40, 8104, (2007)
Details of analysis
Inquiries Regarding Products
Have questions about product implementation? Contact us today.