Dispersed Structure and Nonlinear Structural Analysis of Carbon Nanotubes
The dispersion of carbon nanotubes (CNTs) in microphase-separated structures of block copolymers was simulated using Dissipative Particle Dynamics (DPD), and the obtained structures were meshed for uniaxial tensile analysis using nonlinear Finite Element Method in Ansys LS-DYNA. The analysis captured stress transfer from interfacial debonding to the polymer region, evaluating the effect of dispersion structure on mechanical properties.
Use Cases Highlights
- Evaluation of dispersion structures using DPD
- Structural analysis using Ansys LS-DYNA
- Observation of interfacial debonding and stress transfer
Phase separation and CNT dispersion structures using DPD
DPD simulations of phase separation and CNT dispersion in diblock copolymers are shown. CNTs are modeled to have high affinity with one component and to be rigid, enabling analysis of dispersion behavior.
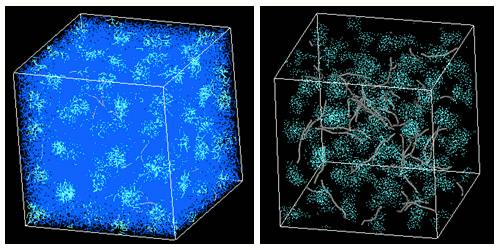
Phase separation of diblock copolymer and dispersion structure of CNTs
Meshed dispersion structures
The dispersion structure of CNTs and polymers obtained from DPD calculations was meshed into a 2D model. Thin cohesive elements were set at the interface, allowing interfacial parameters to be adjusted in Finite Element Method (FEM) analysis.
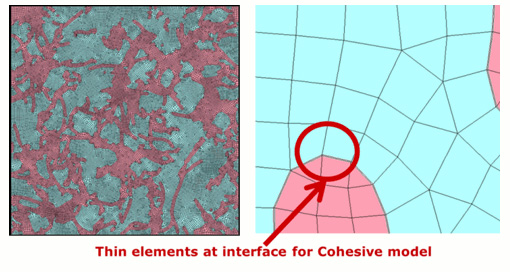
2D mesh data
Deformation analysis using nonlinear Finite Element Method
Uniaxial elongation analysis using nonlinear Finite Element Method (structural analysis) with Ansys LS-DYNA was performed to capture interfacial debonding and stress transfer, clarifying the effect of CNT dispersion structure on stress–strain properties.
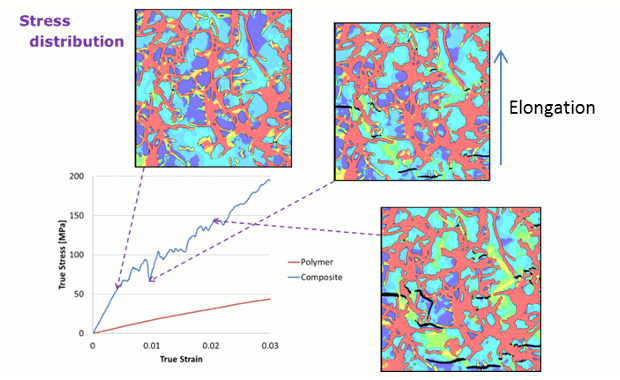
Stress distribution during deformation
Reference
[1] Appl. Phys. Lett., 90, 033116, (2007)
[2] T.Ozawa, The Japan Society for Computational Engineering and Science (JSCES) 17th Annual Conference, (2012)
[2] T.Ozawa, The Japan Society for Computational Engineering and Science (JSCES) 17th Annual Conference, (2012)
Details of analysis
Inquiries Regarding Products
Have questions about product implementation? Contact us today.