Simulation of heat transfer in fiber oriented material using VSOP-PS
The particle method engine VSOP-PS was used to analyze the thermal conductivity of fiber-oriented composite materials. Significant differences in thermal conductivity depending on fiber orientation were confirmed, and similar trends were obtained when compared with Digimat-MF.
Use Cases Highlights
- Creation of fiber orientation structures and evaluation of thermal conductivity using the particle method
- Analysis of the effect of fiber orientation
Creation of fiber-oriented structures and evaluation of thermal conductivity using the particle method
A fiber orientation model created using a particle method is shown. Fibers are placed as particles within a matrix, and shear flow is applied to form an oriented structure. Fibers are modeled as rigid while reproducing a slightly curved shape.
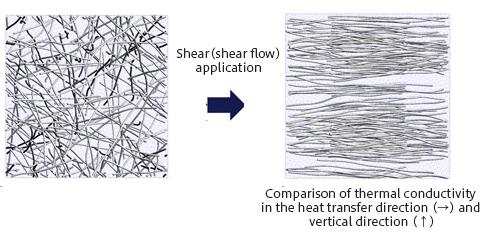
Modeling of fiber orientation structures using particle method
Analysis of the effect of fiber orientation
A comparison of thermal conductivity when fibers are oriented in the heat conduction direction (0°) and perpendicular (90°) is shown. When oriented in the heat conduction direction, thermal conductivity is about three times higher than in the perpendicular direction, indicating a significant effect of orientation.
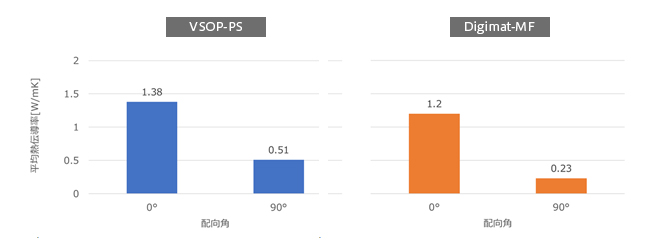
Difference in thermal conductivity depending on orientation direction (VSOP-PS calculation results)
Reference
[1] (in Japanese) https://www.tus.ac.jp/today/archive/20220926_3581.html
[2] (in Japanese) https://www.kri-inc.jp/tech/1273742_11451.html
[3] Digimat-MF
[2] (in Japanese) https://www.kri-inc.jp/tech/1273742_11451.html
[3] Digimat-MF
Details of analysis
Inquiries Regarding Products
Have questions about product implementation? Contact us today.