Dielectric dispersion of water in the GHz frequency range (1)
Full-Atomistic Molecular Dynamics (FAMD) was used to evaluate dielectric dispersion of water. From equilibrium calculations using VSOP, the autocorrelation function of polarization was obtained, and relaxation time was calculated by fitting with a Debye-type relaxation function. The obtained static dielectric constant showed good agreement with literature values, allowing quantitative evaluation of dielectric properties in the GHz range.
Use Cases Highlights
- Evaluation of dielectric dispersion of water by MD
- Calculation of complex permittivity from dielectric relaxation functions
- Agreement with literature values
Evaluation of dielectric dispersion of water using VSOP
The dielectric relaxation function of water obtained using VSOP is shown. The relaxation time τ is calculated by fitting the dielectric relaxation function, derived from the autocorrelation function of polarization, with a Debye-type function.
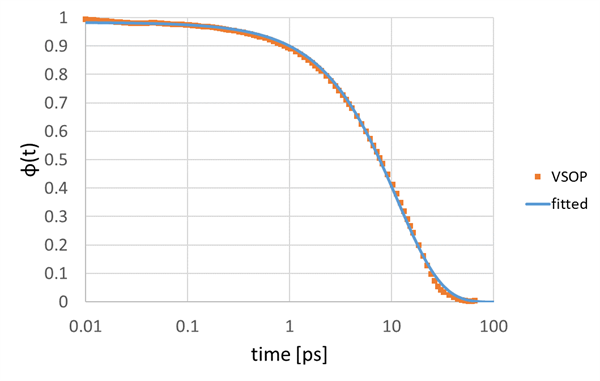
Dielectric relaxation of water
Calculation of complex dielectric constant from dielectric relaxation function
Using relaxation time τ, static dielectric constant ε(0), and high-frequency dielectric constant ε(∞), the dielectric dispersion (complex permittivity) of water in the GHz range is evaluated.
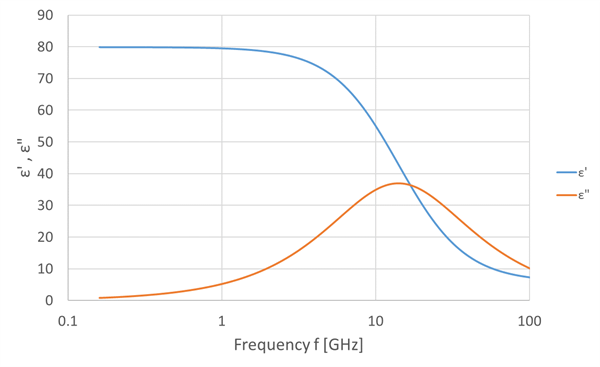
Dielectric dispersion of water
Reference
[1] Chronological Scientific Tables 2005, published by Maruzen
[2] Liebe, H.J. et al, Int J Infrared Milli Waves 12, 659–675 (1991)
[2] Liebe, H.J. et al, Int J Infrared Milli Waves 12, 659–675 (1991)
Inquiries Regarding Products
Have questions about product implementation? Contact us today.