Dielectric relaxation of polymers
- Evaluation of dielectric relaxation from polymer MD simulations
- Analysis of dielectric response from polymer relaxation behavior
- Capability to evaluate complex permittivity
Evaluation of dielectric relaxation from polymer MD calculations
The dipole moment autocorrelation function Φ of cis-polybutadiene at various temperatures and its fitting with the KWW equation are shown. Relaxation becomes slower with decreasing temperature, and the KWW fit enables quantitative evaluation of relaxation times.
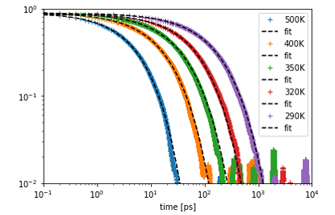
Analysis of dielectric response from polymer relaxation behavior
A graph plotting relaxation time τ calculated from fitting to the KWW equation against the inverse of temperature is shown. This plot demonstrates that relaxation time changes exponentially with temperature, aiding in the understanding of glass transition behavior. Comparisons with data from previous literature are also included.
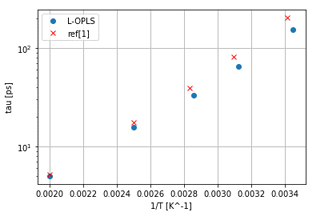
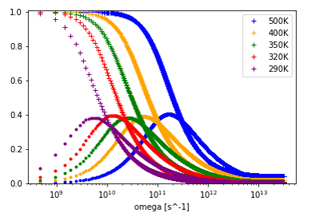
Evaluation of complex dielectric constant
The real and imaginary parts of the dielectric relaxation spectrum obtained by Fourier transforming the autocorrelation function from the KWW equation are shown. This spectrum represents the frequency response characteristics of the material and is used to evaluate the frequency dependence of dielectric loss and permittivity. Comparison with experiments also confirms the model's validity.